Abstract
Background
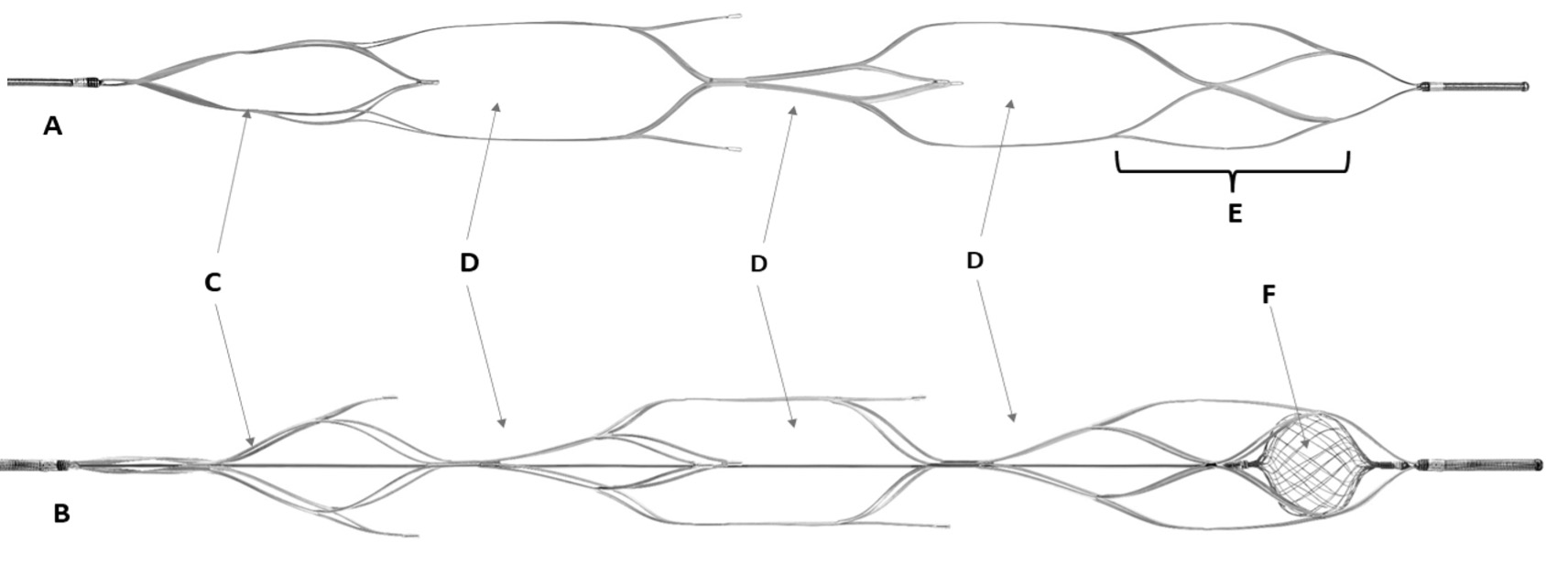
High quality reperfusion is linked to better clinical outcomes during thrombectomy for large vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke. A novel stent-retriever device with an integrated microfilter for embolic distal protection has been developed to improve first pass full reperfusion.
Objective
Compare the safety and effectiveness of the NeVa NET™ versus the standard stent-retriever thrombectomy devices.
Materials and methods
Radial force measurements were performed on 10 NeVa NET™ and 4 Solitaire™ 6x30mm. Animal studies involving three Yorkshire pigs were performed comparing NeVa NET™ to Solitaire™ 6x40mm and 4x40mm to assess for acute vascular injury, vasospasm and thrombogenicity during thrombectomy. A randomized comparison in a closed loop vascular model was performed to quantify first pass effect and distal emboli generated during twenty MCA thrombectomies.
Results
Radial force curves were similar between the NeVa NET™ and Solitaire™ 6x30mm. Below 2.5mm the Solitaire™ demonstrated higher radial force compared to NeVa NET™. Vasospasm scores were nearly identical after four thrombectomies in multiple similar sized swine arteries. The addition of the internal filter did not result in increased thrombogenicity in the non-heparinized swine model. In the randomized flow model study, NeVa NET™ required less passes than Solitaire™ to achieve TICI 3 reperfusion (p=0.0344). Solitaire™ generated 4-fold more clot fragments >1mm in size compared to NeVa Net™ (p=0.037, Wilcoxan rank sum). For fragments between 0.2-1mm, Solitaire™ generated 91 whereas NeVa™ generated a total of 20 fragments. Overall, more clot fragments were generated during Solitaire™ as compared to NeVa NET™ thrombectomy (p=0.048).
Conclusions
Our pre-clinical results support the use of the NeVa NETTM device in a clinical trial to determine if this novel design improves first pass full reperfusion.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of Vascular and Interventional Neurology